Last Updated on January 14, 2021 by Admin
ITN Chapter 4 Quiz Answers Cisco 2019 100%
This quiz covers the content in CCNA R&S Introduction to Networks Chapter 4. It is designed to provide an additional opportunity to practice the skills and knowledge presented in the chapter and to prepare for the Chapter Exam.
-
A network team is comparing topologies for connecting on a shared media. Which physical topology is an example of a hybrid topology for a LAN?
- bus
- extended star
- ring
- partial mesh
Explanation: An extended star topology is an example of a hybrid topology as additional switches are interconnected with other star topologies. A partial mesh topology is a common hybrid WAN topology. The bus and ring are not hybrid topology types.
-
What makes fiber preferable to copper cabling for interconnecting buildings? (Choose three.)
- greater distances per cable run
- lower installation cost
- limited susceptibility to EMI/RFI
- durable connections
- greater bandwidth potential
- easily terminated
-
What is the purpose of the OSI physical layer?
- controlling access to media
- transmitting bits across the local media
- performing error detection on received frames
- exchanging frames between nodes over physical network media
Explanation: The physical layer is responsible for transmitting the actual signals across the physical media as bits. Exchanging frames, controlling media access, and performing error detection are all functions of the data link layer.
-
Which method of data transfer allows information to be sent and received at the same time?
- full duplex
- half duplex
- multiplex
- simplex
-
Match the description with the media. (Not all options are used.)
- STP ——-> This type of copper media is used in industrial or similar environments where there is a lot of interference.
- wireless ——-> This type of media provides the most mobility options.
- optical fiber ——-> This type of media is used for high transmission speed and can also transfer data over long distances.
- coaxial ——-> Traditionally used for television but can now be used in a network to connect the customer location to the wiring of the customer premises.
Explanation: UTP cables are used in wired office environments. Coaxial cables are used to connect cable modems and televisions. Fiber optics are used for high transmission speeds and to transfer data over long distances. STP cables are used in environments where there is a lot of interference.
-
Which statement describes a characteristic of the frame header fields of the data link layer?
- They all include the flow control and logical connection fields.
- Ethernet frame header fields contain Layer 3 source and destination addresses.
- They vary depending on protocols.
- They include information on user applications.
Explanation: All data link layer protocols encapsulate the Layer 3 PDU within the data field of the frame. However, the structure of the frame and the fields that are contained in the header vary according to the protocol. Different data link layer protocols may use different fields, like priority/quality of service, logical connection control, physical link control, flow control, and congestion control.
-
Which two factors influence the method that is used for media access control? (Choose two.)
- how data is generated by end devices applications
- how the connection between nodes appears to the data link layer
- how signals are encoded by the NICs on end devices
- how nodes share the media
- how the IP protocol forwards the packet to the destination
Explanation: The media access control method used depends on the topology (how the connection between the nodes appears to the data link layer), and how the nodes share the media. The type of data generated by end devices applications, the way signals are encoded by the NICs on end devices, and even the way the IP protocol forwards the packet through the network have no influence on the choice of the method used for media access control.
-
What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- CSMA/CD
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CA
- token passing
Explanation: Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) is used with wireless networking technology to mediate media contention. Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) is used with wired Ethernet technology to mediate media contention. Priority ordering and token passing are not used (or not a method) for media access control.
-
Match each type of frame field to its function. (Not all options are used.)
- addressing ——> This field helps to direct the frame toward its destination.
- error detection ——> This field checks if the frame has been damaged during the transfer.
- type ——> This field is used by the LLC to identify the Layer 3 protocol.
- frame start ——> This field identifies the beginning of a frame.
Explanation: Place in the following order:
error detection – This field checks if the frame has been damaged during the transfer.
The second answer is not used.
addressing – This field helps to direct the frame toward its destination.
frame start – This field identifies the beginning of a frame.
type – This field is used by the LLC to identify the Layer 3 protocol.
-
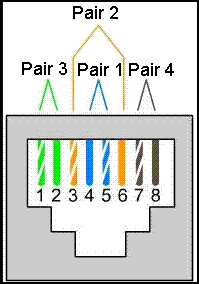
Refer to the exhibit. One end of the cable is terminated as displayed, and the other end is terminated in accordance with the T568A standard. What type of cable would be created in this manner?
- crossover
- rollover
- straight-through
- fiber-optic
Explanation: A straight-through cable can have either a T568A or T568B standard termination at one end and the same at the other end. A crossover cable has a T568A standard termination at one end and a T568B standard at the other end. A rollover cable can have either a T568A or T568B standard termination at one end, and at the other end have the same standard, but with the wires connected in reverse order. A fiber-optic cable is not terminated using RJ-45 connectors.
-
A network administrator is designing a new network infrastructure that includes both wired and wireless connectivity. Under which situation would a wireless connection be recommended?
- The end-user device only has an Ethernet NIC.
- The end-user device requires a dedicated connection because of performance requirements.
- The end-user device needs mobility when connecting to the network.
- The end-user device area has a high concentration of RFI.
Explanation: When the end-user devices need mobility to connect to the network, wireless is recommended. If an end-user device only has an Ethernet NIC, the user will only be able to use Ethernet cabling. If RFI is an issue, wireless is not recommended. An end-user device that requires a dedicated connection for performance would perform better with a dedicated Ethernet cable.
-
What type of cable is used to connect a workstation serial port to a Cisco router console port?
- crossover
- rollover
- straight-through
- coaxial
Explanation: UTP cable wire pairs can be terminated in different configurations for use in different applications. To use a UTP cable for consoling into a Cisco router from a PC serial port, it must be terminated as a rollover or console cable.
-
Fill in the blank.
In fiber optic media, the signals are represented as patterns of LIGHT .
- Noted: There are 3 possible answers. You can fill in one of the following in netacad: LIGHT, Light, and light. But you can fill only LIGHT.
Explanation: In fiber optic media, the physical layer produces the representation and groupings of bits as patterns of light.
- Noted: There are 3 possible answers. You can fill in one of the following in netacad: LIGHT, Light, and light. But you can fill only LIGHT.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What is the maximum possible throughput between the PC and the server?
- 128 kb/s
- 10 Mb/s
- 100 Mb/s
- 1000 Mb/s
Explanation: The maximum throughput between any two nodes on a network is determined by the slowest link between those nodes.
-
Which statement correctly describes frame encoding?
- It uses the characteristic of one wave to modify another wave.
- It transmits data signals along with a clock signal which occurs at evenly spaced time durations.
- It generates the electrical, optical, or wireless signals that represent the binary numbers of the frame.
- It converts bits into a predefined code in order to provide a predictable pattern to help distinguish data bits from control bits.
Explanation: Frame encoding converts a stream of data bits into a predefined code that is recognized by both the sender and receiver. These codes are used for a variety of purposes, such as distinguishing data bits from control bits, and identifying the beginning and end of a frame.
-
What is a characteristic of a WAN hub-and-spoke topology?
- It requires that some of the branch sites be interconnected through point-to-point links.
- It requires that every site be interconnected to each other through point-to-point links.
- All sites require a hub device that connects to a router.
- The branch sites are connected to a central site through point-to-point links.
Explanation: A hub-and-spoke topology is a WAN version of the star topology in which a central site interconnects branch sites using point-to-point links. A mesh topology requires that every end system be interconnected to every other system using point-to-point links. A partial mesh is a variation of this topology, where some but not all end devices are interconnected. There is no topology where all the sites have to have hub devices that are connected to a router.
-
Which is a function of the Logical Link Control (LLC) sublayer?
- to define the media access processes that are performed by the hardware
- to provide data link layer addressing
- to identify which network layer protocol is being used
- to accept segments and package them into data units that are called packets
Explanation: Defining the media access processes that are performed by the hardware and providing data link layer addressing are functions of the MAC sublayer. The data link layer accepts Layer 3 packets and packages them into data units that are called frames.