Last Updated on January 14, 2021 by Admin
CCNA 1 v6.0 ITN Final Exam Form A Answers 2019
Cisco CCNA 1 ITN v6.0 Final Exam Answers Routing and Switching (R&S) Introduction to Networks (ITN) (Version 6.00) collection year 2018 and 2019 Full 100%. CCNA 1 has been know as ITN. The following are the questions exam answers. Guarantee Passed. CCNA 1 v6.0 final exam answers has no new update from the old version 5.1. You can review all Final Exam Answers. You will get passed scored 100% with this version 6.0. Good Luck for ITN v6.0 Exam!
-
What is a characteristic of a fault tolerant network?
- a network that protects confidential information from unauthorized access
- a network that can expand quickly to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service delivered to existing users
- a network that supports a mechanism for managing congestion and ensuring reliable delivery of content to all users
- a network that recovers quickly when a failure occurs and depends on redundancy to limit the impact of a failure
Explanation: Fault tolerant networks limit the impact of a failure because the networks are built in a way that allows for quick recovery when such a failure occurs. These networks depend on multiple or redundant paths between the source and destination of a message.
A scalable network can expand quickly to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users.
Quality of service (QoS) is a mechanism for managing congestion and ensuring reliable delivery of content to all users.
-
Three bank employees are using the corporate network. The first employee uses a web browser to view a company web page in order to read some announcements. The second employee accesses the corporate database to perform some financial transactions. The third employee participates in an important live audio conference with other corporate managers in branch offices. If QoS is implemented on this network, what will be the priorities from highest to lowest of the different data types?
- audio conference, financial transactions, web page
- financial transactions, web page, audio conference
- audio conference, web page, financial transactions
- financial transactions, audio conference, web page
Explanation: QoS mechanisms enable the establishment of queue management strategies that enforce priorities for different categories of application data. Thus, this queuing enables voice data to have priority over transaction data, which has priority over web data.
-
What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
Explanation: Cloud computing extends IT’s capabilities without requiring investment in new infrastructure, training new personnel, or licensing new software. These services are available on-demand and delivered economically to any device anywhere in the world without compromising security or function. BYOD is about end users having the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business or campus network. Smart home technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated. Powerline networking is a trend for home networking that uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
-
What is the function of the shell in an OS?
- It interacts with the device hardware.
- It interfaces between the users and the kernel.
- It provides dedicated firewall services.
- It provides the intrusion protection services for the device.
Explanation: Most operating systems contain a shell and a kernel. The kernel interacts with the hardware and the shell interfaces between the kernel and the users.
-
Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco switch?
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection
Explanation: A CLI session using Secure Shell (SSH) provides enhanced security because SSH supports strong passwords and encryption during the transport of session data. The other methods support authentication but not encryption.
-
A network technician is attempting to configure an interface by entering the following command: SanJose(config)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0. The command is rejected by the device. What is the reason for this?
- The command is being entered from the wrong mode of operation.
- The command syntax is wrong.
- The subnet mask information is incorrect.
- The interface is shutdown and must be enabled before the switch will accept the IP address.
Explanation: The wrong mode of operation is being used. The CLI prompt indicates that the mode of operation is global configuration. IP addresses must be configured from interface configuration mode, as indicated by the SanJose(config-if)# prompt.
-
An administrator uses the Ctrl-Shift-6 key combination on a switch after issuing the ping command. What is the purpose of using these keystrokes?
- to restart the ping process
- to interrupt the ping process
- to exit to a different configuration mode
- to allow the user to complete the command
Explanation: To interrupt an IOS process such as ping or traceroute, a user enters the Ctrl-Shift-6 key combination. Tab completes the remainder of parameters or arguments within a command. To exit from configuration mode to privileged mode use the Ctrl-Z keystroke. CTRL-R will redisplay the line just typed, thus making it easier for the user to press Enter and reissue the ping command.
-
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is configuring access control to switch SW1. If the administrator uses a console connection to connect to the switch, which password is needed to access user EXEC mode?
- letmein
- secretin
- lineconin
- linevtyin
Explanation: Telnet accesses a network device through the virtual interface configured with the line VTY command. The password configured under this is required to access the user EXEC mode. The password configured under the line console 0 command is required to gain entry through the console port, and the enable and enable secret passwords are used to allow entry into the privileged EXEC mode.
-
On which switch interface would an administrator configure an IP address so that the switch can be managed remotely?
- FastEthernet0/1
- VLAN 1
- vty 0
- console 0
Explanation: Interface VLAN 1 is a virtual interface on a switch, called SVI (switch virtual interface). Configuring an IP address on the default SVI, interface VLAN 1, will allow a switch to be accessed remotely. The VTY line must also be configured to allow remote access, but an IP address cannot be configured on this line.
-
What protocol is responsible for controlling the size of segments and the rate at which segments are exchanged between a web client and a web server?
- TCP
- IP
- HTTP
- Ethernet
Explanation: TCP is a Layer 4 protocol of the OSI model. TCP has several responsibilities in the network communication process. It divides large messages into smaller segments which are more efficient to send across the network. It also controls the size and rate of segments exchanged between clients and servers.
-
What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- A company can monopolize the market.
- The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor.
- An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- It encourages competition and promotes choices.
Explanation: A monopoly by one company is not a good idea from a user point of view. If a protocol can only be run on one brand, it makes it difficult to have mixed equipment in a network. A proprietary protocol is not free to use. An open standard protocol will in general be implemented by a wide range of vendors.
-
What are two benefits of using a layered network model? (Choose two.)
- It assists in protocol design.
- It speeds up packet delivery.
- It prevents designers from creating their own model.
- It prevents technology in one layer from affecting other layers.
- It ensures a device at one layer can function at the next higher layer.
Explanation: Some vendors have developed their own reference models and protocols. Today, if a device is to communicate on the Internet, the device must use the TCP/IP model. The benefits of using a layered model are as follows:
- assists in protocol design
- fosters competition between vendors
- prevents a technology that functions at one layer from affecting any other layer
- provides a common language for describing network functionality
- helps in visualizing the interaction between each layer and protocols between each layer
-
Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as two layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- data link
- network
- physical
- session
- transport
Explanation: The OSI transport layer is functionally equivalent to the TCP/IP transport layer, and the OSI network layer is equivalent to the TCP/IP internet layer. The OSI data link and physical layers together are equivalent to the TCP/IP network access layer. The OSI session layer (with the presentation layer) is included within the TCP/IP application layer.
-
Which name is assigned to the transport layer PDU?
- bits
- data
- frame
- packet
- segment
Explanation: Application data is passed down the protocol stack on its way to be transmitted across the network media. During the process, various protocols add information to it at each level. At each stage of the process, a PDU (protocol data unit) has a different name to reflect its new functions. The PDUs are named according to the protocols of the TCP/IP suite:
- Data – The general term for the PDU used at the application layer.
- Segment – transport layer PDU
- Packet – network layer PDU
- Frame – data link layer PDU
- Bits – A physical layer PDU used when physically transmitting data over the medium
-
A network administrator is troubleshooting connectivity issues on a server. Using a tester, the administrator notices that the signals generated by the server NIC are distorted and not usable. In which layer of the OSI model is the error categorized?
- presentation layer
- network layer
- physical layer
- data link layer
Explanation: The NIC has responsibilities in both Layer 1 and Layer 2. The NIC encodes the frame as a series of signals that are transmitted onto the local media. This is the responsibility of the physical layer of the OSI model. The signal could be in the form of electrical, optical, or radio waves.
-
A network administrator is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical financial application. The administrator notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
Explanation: Throughput usually does not match the specified bandwidth of physical links due to multiple factors. These factors include, the amount of traffic, type of traffic, and latency created by the network devices the data has to cross.
-
What is a characteristic of UTP cabling?
- cancellation
- cladding
- immunity to electrical hazards
- woven copper braid or metallic foil
Explanation: Cladding and immunization from electrical hazards are characteristics for fiber-optic cabling. A woven copper braid or metallic foil is used as a shield for the inner coaxial cable conductor. Cancellation is a property of UTP cabling where two wires are located adjacent to one another so each magnetic field cancels out the adjacent magnetic field.
-
What are two characteristics of fiber-optic cable? (Choose two.)
- It is not affected by EMI or RFI.
- Each pair of cables is wrapped in metallic foil.
- It combines the technique of cancellation, shielding, and twisting to protect data.
- It typically contains 4 pairs of fiber-optic wires.
- It is more expensive than UTP cabling is.
Explanation: Fiber-optic cabling supports higher bandwidth than UTP for longer distances. Fiber is immune to EMI and RFI, but costs more, requires more skill to install, and requires more safety precautions.
-
What is a characteristic of the LLC sublayer?
- It provides the logical addressing required that identifies the device.
- It provides delimitation of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium.
- It places information in the frame allowing multiple Layer 3 protocols to use the same network interface and media.
- It defines software processes that provide services to the physical layer.
Explanation: The Logical Link Control (LLC) defines the software processes that provide services to the network layer protocols. The information is placed by LLC in the frame and identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame. This information allows multiple Layer 3 protocols, such as IPv4 and IPv6, to utilize the same network interface and media.
-
A network team is comparing physical WAN topologies for connecting remote sites to a headquarters building. Which topology provides high availability and connects some, but not all, remote sites?
- mesh
- partial mesh
- hub and spoke
- point-to-point
Explanation: Partial mesh topologies provide high availability by interconnecting multiple remote sites, but do not require a connection between all remote sites. A mesh topology requires point-to-point links with every system being connected to every other system. A point-to-point topology is where each device is connected to one other device. A hub and spoke uses a central device in a star topology that connects to other point-to-point devices.
-
What method is used to manage contention-based access on a wireless network?
- CSMA/CD
- priority ordering
- CSMA/CA
- token passing
Explanation: Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) is used with wireless networking technology to mediate media contention. Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) is used with wired Ethernet technology to mediate media contention. Priority ordering and token passing are not used (or not a method) for media access control.
-
What are the three primary functions provided by Layer 2 data encapsulation? (Choose three.)
- error correction through a collision detection method
- session control using port numbers
- data link layer addressing
- placement and removal of frames from the media
- detection of errors through CRC calculations
- delimiting groups of bits into frames
- conversion of bits into data signals
Explanation: Through the framing process, delimiters are used to identify the start and end of the sequence of bits that make up a frame. Data link layer addressing is added to enable a frame to be delivered to a destination node. A cyclic redundancy check (CRC) field is calculated on every bit and added to the frame. If the CRC value contained in the arriving frame is the same as the one the receiving node creates, the frame will be processed.
-
What will a host on an Ethernet network do if it receives a frame with a destination MAC address that does not match its own MAC address?
- It will discard the frame.
- It will forward the frame to the next host.
- It will remove the frame from the media.
- It will strip off the data-link frame to check the destination IP address.
Explanation: In an Ethernet network, each NIC in the network checks every arriving frame to see if the destination MAC address in the frame matches its own MAC address. If there is no match, the device discards the frame. If there is a match, the NIC passes the frame up to the next OSI layer.
-
Which frame forwarding method receives the entire frame and performs a CRC check to detect errors before forwarding the frame?
- cut-through switching
- store-and-forward switching
- fragment-free switching
- fast-forward switching
Explanation: Fast-forward and fragment-free switching are variations of cut-through switching, which begins to forward the frame before the entire frame is received.
-
Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
- DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
- 172.168.10.99
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- 172.168.10.65
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
Explanation: When a host sends information to a distant network, the Layer 2 frame header will contain a source and destination MAC address. The source address will be the originating host device. The destination address will be the router interface that connects to the same network. In the case of host A sending information to host B, the source address is AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA and the destination address is the MAC address assigned to the R2 Ethernet interface, BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB.
-
What addresses are mapped by ARP?
- destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address
- destination IPv4 address to the source MAC address
- destination IPv4 address to the destination host name
- destination MAC address to the source IPv4 address
Explanation: ARP, or the Address Resolution Protocol, works by mapping a destination MAC address to a destination IPv4 address. The host knows the destination IPv4 address and uses ARP to resolve the corresponding destination MAC address.
-
What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
- performing error detection
- routing packets toward the destination
- encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer
- placement of frames on the media
- collision detection
Explanation: The OSI network layer provides several services to allow communication between devices:
- addressing
- encapsulation
- routing
- de-encapsulation
Error detection, placing frames on the media, and collision detection are all functions of the data ink layer.
-
What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
- to store the routing table
- to retain contents when power is removed
- to store the startup configuration file
- to contain the running configuration file
- to store the ARP table
Explanation: NVRAM is permanent memory storage, so the startup configuration file is preserved even if the router loses power.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What will be the result of entering this configuration the next time a network administrator connects a console cable to the router and no additional commands have been entered?
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco123.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco234.
- The administrator will be required to enter Cisco789.
- The administrator will be presented with the R1> prompt.
Explanation: Until both the password password and the login commands are entered in console line configuration mode, no password is required to gain access to enable mode.
-
What is the dotted decimal representation of the IPv4 address 11001011.00000000.01110001.11010011?
- 192.0.2.199
- 198.51.100.201
- 203.0.113.211
- 209.165.201.223
Explanation: Each section (octet) contains eight binary digits. Each digit represents a specific value (128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, and 1). Everywhere there is a 1, the specific value is relevant. Add all relevant values in a particular octet to obtain the decimal value. For example binary 11001011 equals 203 in decimal.
-
What are three characteristics of multicast transmission? (Choose three.)
- The source address of a multicast transmission is in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- A single packet can be sent to a group of hosts.
- Multicast transmission can be used by routers to exchange routing information.
- Routers will not forward multicast addresses in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
- Computers use multicast transmission to request IPv4 addresses.
- Multicast messages map lower layer addresses to upper layer addresses.
Explanation: Broadcast messages consist of single packets that are sent to all hosts on a network segment. These types of messages are used to request IPv4 addresses, and map upper layer addresses to lower layer addresses. A multicast transmission is a single packet sent to a group of hosts and is used by routing protocols, such as OSPF and RIPv2, to exchange routes. The address range 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255 is reserved for link-local addresses to reach multicast groups on a local network.
-
What are the three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for internal private use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 64.100.0.0/14
- 127.16.0.0/12
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.31.7.0/24
- 192.168.0.0/16
Explanation: The private IP address blocks that are used inside companies are as follows:
- 10.0.0.0 /8 (any address that starts with 10 in the first octet)
- 172.16.0.0 /12 (any address that starts with 172.16 in the first two octets through 172.31.255.255)
- 192.168.0.0 /16 (any address that starts with 192.168 in the first two octets)
-
What purpose does NAT64 serve in IPv6?
- It converts IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.
- It translates private IPv6 addresses into public IPv6 addresses.
- It enables companies to use IPv6 unique local addresses in the network.
- It converts regular IPv6 addresses into 64-bit addresses that can be used on the Internet.
- It converts the 48-bit MAC address into a 64-bit host address that can be used for automatic host addressing.
Explanation: NAT64 is typically used in IPv6 when networks are being transitioned from IPv4 to IPv6. It allows the IPv6 networks to connect to IPv4 networks (such as the Internet), and works by translating the IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.
-
What is the most compressed representation of the IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001?
- 2001:0:abcd::1
- 2001:0:0:abcd::1
- 2001::abcd::1
- 2001:0000:abcd::1
- 2001::abcd:0:1
Explanation: The IPv6 address 2001:0000:0000:abcd:0000:0000:0000:0001 in its most compressed format would be 2001:0:0:abcd::1. The first two hextets of zeros would each compress to a single zero. The three consecutive hextets of zeros can be compressed to a double colon ::. The three leading zeros in the last hextet can be removed. The double colon :: can only be used once in an address.
-
Which range of link-local addresses can be assigned to an IPv6-enabled interface?
- FEC0::/10
- FDEE::/7
- FE80::/10
- FF00::/8
Explanation: Link-local addresses are in the range of FE80::/10 to FEBF::/10. The original IPv6 specification defined site-local addresses and used the prefix range FEC0::/10, but these addresses were deprecated by the IETF in favor of unique local addresses. FDEE::/7 is a unique local address because it is in the range of FC00::/7 to FDFF::/7. IPv6 multicast addresses have the prefix FF00::/8.
-
How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
- 254
- 190
- 192
- 62
- 64
Explanation: When a /26 mask is used, 6 bits are used as host bits. With 6 bits, 64 addresses are possible, but one address is for the subnet number and one address is for a broadcast. This leaves 62 addresses that can be assigned to network devices.
-
A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
Explanation: The subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 has 8 host bits. The mask of 255.255.255.128 results in 7 host bits. The mask of 255.255.255.224 has 5 host bits. Finally, 255.255.255.240 represents 4 host bits.
-
Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
Explanation: For the subnet of 192.168.1.64/26, there are 6 bits for host addresses, yielding 64 possible addresses. However, the first and last subnets are the network and broadcast addresses for this subnet. Therefore, the range of host addresses for this subnet is 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126. The other subnets do not contain the address 192.168.1.96 as a valid host address.
-
Which statement is true about variable-length subnet masking?
- Each subnet is the same size.
- The size of each subnet may be different, depending on requirements.
- Subnets may only be subnetted one additional time.
- Bits are returned, rather than borrowed, to create additional subnets.
Explanation: In variable-length subnet masking, bits are borrowed to create subnets. Additional bits may be borrowed to create additional subnets within the original subnets. This may continue until there are no bits available to borrow.
-
Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
Explanation: The source and destination port numbers are used to identify the correct application and window within that application.
-
A user opens three browsers on the same PC to access www.cisco.com to search for certification course information. The Cisco web server sends a datagram as a reply to the request from one of the web browsers. Which information is used by the TCP/IP protocol stack in the PC to identify which of the three web browsers should receive the reply?
- the destination IP address
- the destination port number
- the source IP address
- the source port number
Explanation: Each web browser client application opens a randomly generated port number in the range of the registered ports and uses this number as the source port number in the datagram that it sends to a server. The server then uses this port number as the destination port number in the reply datagram that it sends to the web browser. The PC that is running the web browser application receives the datagram and uses the destination port number that is contained in this datagram to identify the client application.
-
What are two ways that TCP uses the sequence numbers in a segment? (Choose two.)
- to identify missing segments at the destination
- to reassemble the segments at the remote location
- to specify the order in which the segments travel from source to destination
- to limit the number of segments that can be sent out of an interface at one time
- to determine if the packet changed during transit
-
Which two tasks are functions of the presentation layer? (Choose two.)
- compression
- addressing
- encryption
- session control
- authentication
Explanation: The presentation layer deals with common data format. Encryption, formatting, and compression are some of the functions of the layer. Addressing occurs in the network layer, session control occurs in the session layer, and authentication takes place in the application or session layer.
-
What is a key characteristic of the peer-to-peer networking model?
- wireless networking
- social networking without the Internet
- network printing using a print server
- resource sharing without a dedicated server
Explanation: The peer-to-peer (P2P) networking model allows data, printer, and resource sharing without a dedicated server.
-
A technician can ping the IP address of the web server of a remote company but cannot successfully ping the URL address of the same web server. Which software utility can the technician use to diagnose the problem?
- tracert
- ipconfig
- netstat
- nslookup
Explanation: Traceroute (tracert) is a utility that generates a list of hops that were successfully reached along the path from source to destination.This list can provide important verification and troubleshooting information. The ipconfig utility is used to display the IP configuration settings on a Windows PC. The Netstat utility is used to identify which active TCP connections are open and running on a networked host. Nslookup is a utility that allows the user to manually query the name servers to resolve a given host name. This utility can also be used to troubleshoot name resolution issues and to verify the current status of the name servers.
-
Which domain name would be an example of a top-level domain?
- www.cisco.com
- cisco.com
- .com
- root.cisco.com
Explanation: Top-level domains represent a country or type of organization, such as .com or .edu.
-
A PC obtains its IP address from a DHCP server. If the PC is taken off the network for repair, what happens to the IP address configuration?
- The configuration is permanent and nothing changes.
- The address lease is automatically renewed until the PC is returned.
- The address is returned to the pool for reuse when the lease expires.
- The configuration is held by the server to be reissued when the PC is returned.
Explanation: When a DCHP address is issued to a host, it is for a specific lease time. Once the lease expires, the address is returned to the DHCP pool.
-
A wireless host needs to request an IP address. What protocol would be used to process the request?
- FTP
- HTTP
- DHCP
- ICMP
- SNMP
Explanation: The DHCP protocol is used to request, issue, and manage IP addressing information. CSMA/CD is the access method used with wired Ethernet. ICMP is used to test connectivity. SNMP is used with network management and FTP is used for file transfer.
-
Which example of malicious code would be classified as a Trojan horse?
- malware that was written to look like a video game
- malware that requires manual user intervention to spread between systems
- malware that attaches itself to a legitimate program and spreads to other programs when launched
- malware that can automatically spread from one system to another by exploiting a vulnerability in the target
Explanation: A Trojan horse is malicious code that has been written specifically to look like a legitimate program. This is in contrast to a virus, which simply attaches itself to an actual legitimate program. Viruses require manual intervention from a user to spread from one system to another, while a worm is able to spread automatically between systems by exploiting vulnerabilities on those devices.
-
When applied to a router, which command would help mitigate brute-force password attacks against the router?
- exec-timeout 30
- service password-encryption
- banner motd $Max failed logins = 5$
- login block-for 60 attempts 5 within 60
Explanation: The login block-for command sets a limit on the maximum number of failed login attempts allowed within a defined period of time. If this limit is exceeded, no further logins are allowed for the specified period of time. This helps to mitigate brute-force password cracking since it will significantly increase the amount of time required to crack a password. The exec-timeout command specifies how long the session can be idle before the user is disconnected. The service password-encryption command encrypts the passwords in the running configuration. The banner motd command displays a message to users who are logging in to the device.
-
A network technician suspects that a particular network connection between two Cisco switches is having a duplex mismatch. Which command would the technician use to see the Layer 1 and Layer 2 details of a switch port?
- show interfaces
- show running-config
- show ip interface brief
- show mac-address-table
Explanation: The show interfaces command can be used on both routers and switches to see speed, duplex, media type, MAC address, port type, and other Layer 1/Layer 2-related information.
-
Where are Cisco IOS debug output messages sent by default?
- memory buffers
- vty lines
- Syslog server
- console line
Explanation: Debug messages, like other IOS log messages, are sent to the console line by default. Sending these messages to the terminal lines requires the terminal monitor command.
-
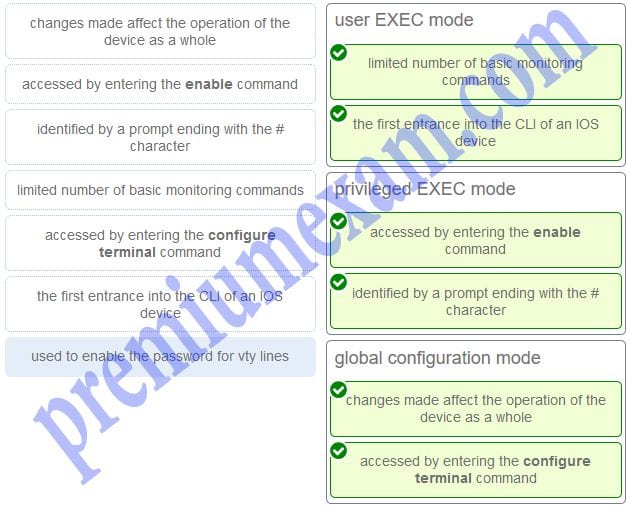
Match the description with the associated IOS mode. (Not all options are used.)
-
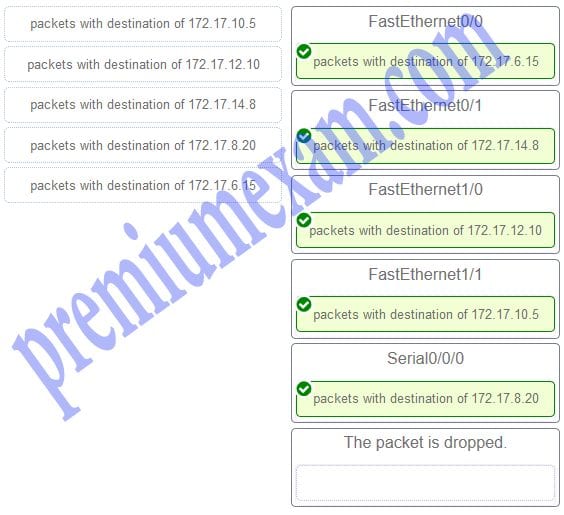
Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
Explanation:
Packets with a destination of 172.17.6.15 are forwarded through Fa0/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.10.5 are forwarded through Fa1/1. Packets with a destination of 172.17.12.10 are forwarded through Fa1/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.14.8 are forwarded through Fa0/1. Because network 172.17.8.0 has no entry in the routing table, it will take the gateway of last resort, which means that packets with a destination of 172.17.8.20 are forwarded through Serial0/0/0. Because a gateway of last resort exists, no packets will be dropped.