Last Updated on January 14, 2021 by Admin
CCNA 1 v6.0 ITN Final Exam Form B Answers 2019
Cisco CCNA 1 ITN v6.0 Final Exam Answers Routing and Switching (R&S) Introduction to Networks (ITN) (Version 6.00) collection year 2018 and 2019 Full 100%. CCNA 1 has been know as ITN. The following are the questions exam answers. Guarantee Passed. CCNA 1 v6.0 final exam answers has no new update from the old version 5.1. You can review all Final Exam Answers. You will get passed scored 100% with this version 6.0. Good Luck for ITN v6.0 Exam!
-
A medium-sized business is researching available options for connecting to the Internet. The company is looking for a high speed option with dedicated, symmetric access. Which connection type should the company choose?
- DSL
- dialup
- satellite
- leased line
- cable modem
-
What is the purpose of having a converged network?
- to provide high speed connectivity to all end devices
- to make sure that all types of data packets will be treated equally
- to achieve fault tolerance and high availability of data network infrastructure devices
- to reduce the cost of deploying and maintaining the communication infrastructure
Explanation: With the development of technology, companies can now consolidate disparate networks onto one platform called a converged network. In a converged network, voice, video, and data travel over the same network, thus eliminating the need to create and maintain separate networks. This also reduces the costs associated with providing and maintaining the communication network infrastructure.
-
What characteristic of a network enables it to quickly grow to support new users and applications without impacting the performance of the service being delivered to existing users?
- reliability
- scalability
- quality of service
- accessibility
Explanation: Networks must be able to quickly grow to support new users and services, without impacting existing users and services. This ability to grow is known as scalability.
-
Which connection provides a secure CLI session with encryption to a Cisco switch?
- a console connection
- an AUX connection
- a Telnet connection
- an SSH connection
Explanation: A CLI session using Secure Shell (SSH) provides enhanced security because SSH supports strong passwords and encryption during the transport of session data. The other methods support authentication but not encryption.
-
A network technician is attempting to configure an interface by entering the following command: SanJose(config)# ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0. The command is rejected by the device. What is the reason for this?
- The command is being entered from the wrong mode of operation.
- The command syntax is wrong.
- The subnet mask information is incorrect.
- The interface is shutdown and must be enabled before the switch will accept the IP address.
Explanation: The wrong mode of operation is being used. The CLI prompt indicates that the mode of operation is global configuration. IP addresses must be configured from interface configuration mode, as indicated by the SanJose(config-if)# prompt.
-
After several configuration changes are made to a router, the copy running-configuration startup-configuration command is issued. Where will the changes be stored?
- flash
- ROM
- NVRAM
- RAM
- the configuration register
- a TFTP server
-
Refer to the exhibit. From global configuration mode, an administrator is attempting to create a message-of-the-day banner by using the command banner motd V Authorized access only! Violators will be prosecuted! V When users log in using Telnet, the banner does not appear correctly. What is the problem?
- The banner message is too long.
- The delimiting character appears in the banner message.
- The symbol “!” signals the end of a banner message.
- Message-of-the-day banners will only appear when a user logs in through the console port.
-
What are three characteristics of an SVI? (Choose three.)
- It is designed as a security protocol to protect switch ports.
- It is not associated with any physical interface on a switch.
- It is a special interface that allows connectivity by different types of media.
- It is required to allow connectivity by any device at any location.
- It provides a means to remotely manage a switch.
- It is associated with VLAN1 by default.
Explanation: Switches have one or more switch virtual interfaces (SVIs). SVIs are created in software since there is no physical hardware associated with them. Virtual interfaces provide a means to remotely manage a switch over a network that is using IP. Each switch comes with one SVI appearing in the default configuration “out-of-the-box.” The default SVI interface is VLAN1.
-
A technician configures a switch with these commands:
SwitchA(config)# interface vlan 1
SwitchA(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
SwitchA(config-if)# no shutdownWhat is the technician configuring?
- Telnet access
- SVI
- password encryption
- physical switchport access
Explanation: For a switch to have an IP address, a switch virtual interface must be configured. This allows the switch to be managed remotely over the network.
-
In computer communication, what is the purpose of message encoding?
- to convert information to the appropriate form for transmission
- to interpret information
- to break large messages into smaller frames
- to negotiate correct timing for successful communication
Explanation: Before a message is sent across a network it must first be encoded. Encoding is the process of converting the data message into another format suitable for transmission across the physical medium. Each bit of the message is encoded into a pattern of sounds, light waves, or electrical impulses depending on the network media over which the bits are transmitted. The destination host receives and decodes the signals in order to interpret the message.
-
What protocol is responsible for controlling the size of segments and the rate at which segments are exchanged between a web client and a web server?
- TCP
- IP
- HTTP
- Ethernet
Explanation: TCP is a Layer 4 protocol of the OSI model. TCP has several responsibilities in the network communication process. It divides large messages into smaller segments which are more efficient to send across the network. It also controls the size and rate of segments exchanged between clients and servers.
-
What are two benefits of using a layered network model? (Choose two.)
- It assists in protocol design.
- It speeds up packet delivery.
- It prevents designers from creating their own model.
- It prevents technology in one layer from affecting other layers.
- It ensures a device at one layer can function at the next higher layer.
Explanation: Some vendors have developed their own reference models and protocols. Today, if a device is to communicate on the Internet, the device must use the TCP/IP model. The benefits of using a layered model are as follows:
- assists in protocol design
- fosters competition between vendors
- prevents a technology that functions at one layer from affecting any other layer
- provides a common language for describing network functionality
- helps in visualizing the interaction between each layer and protocols between each layer
-
What is the process of dividing a data stream into smaller pieces before transmission?
- segmentation
- encapsulation
- encoding
- flow control
Explanation: Data streams would cause significant network congestion if they were transmitted as a single large stream of bits. To increase efficiency, data streams are segmented into smaller more manageable pieces which are then transmitted over the network.
-
When IPv4 addressing is manually configured on a web server, which property of the IPv4 configuration identifies the network and host portion for an IPv4 address?
- DNS server address
- subnet mask
- default gateway
- DHCP server address
Explanation: There are several components that need to be entered when configuring IPv4 for an end device:
- IPv4 address – uniquely identifies an end device on the network
- Subnet mask – determines the network address portion and host portion for an IPv4 address
- Default gateway – the IP address of the router interface used for communicating with hosts in another network
- DNS server address – the IP address of the Domain Name System (DNS) server
DHCP server address (if DHCP is used) is not configured manually on end devices. It will be provided by a DHCP server when an end device requests an IP address.
-
A network administrator is troubleshooting connectivity issues on a server. Using a tester, the administrator notices that the signals generated by the server NIC are distorted and not usable. In which layer of the OSI model is the error categorized?
- presentation layer
- network layer
- physical layer
- data link layer
Explanation: The NIC has responsibilities in both Layer 1 and Layer 2. The NIC encodes the frame as a series of signals that are transmitted onto the local media. This is the responsibility of the physical layer of the OSI model. The signal could be in the form of electrical, optical, or radio waves.
-
A network engineer is measuring the transfer of bits across the company backbone for a mission critical database application. The engineer notices that the network throughput appears lower than the bandwidth expected. Which three factors could influence the differences in throughput? (Choose three.)
- the amount of traffic that is currently crossing the network
- the sophistication of the encapsulation method applied to the data
- the type of traffic that is crossing the network
- the latency that is created by the number of network devices that the data is crossing
- the bandwidth of the WAN connection to the Internet
- the reliability of the gigabit Ethernet infrastructure of the backbone
Explanation: Throughput usually does not match the specified bandwidth of physical links due to multiple factors. These factors include, the amount of traffic, type of traffic, and latency created by the network devices the data has to cross.
-
Which type of UTP cable is used to connect a PC to a switch port?
- console
- rollover
- crossover
- straight-through
Explanation: A rollover cable is a Cisco proprietary cable used to connect to a router or switch console port. A straight-through (also called patch) cable is usually used to interconnect a host to a switch and a switch to a router. A crossover cable is used to interconnect similar devices together, for example, between two switches, two routers, and two hosts.
-
What is a characteristic of the LLC sublayer?
- It provides the logical addressing required that identifies the device.
- It provides delimitation of data according to the physical signaling requirements of the medium.
- It places information in the frame allowing multiple Layer 3 protocols to use the same network interface and media.
- It defines software processes that provide services to the physical layer.
Explanation: The Logical Link Control (LLC) defines the software processes that provide services to the network layer protocols. The information is placed by LLC in the frame and identifies which network layer protocol is being used for the frame. This information allows multiple Layer 3 protocols, such as IPv4 and IPv6, to utilize the same network interface and media.
-
What are the three primary functions provided by Layer 2 data encapsulation? (Choose three.)
- error correction through a collision detection method
- session control using port numbers
- data link layer addressing
- placement and removal of frames from the media
- detection of errors through CRC calculations
- delimiting groups of bits into frames
- conversion of bits into data signals
Explanation: Through the framing process, delimiters are used to identify the start and end of the sequence of bits that make up a frame. Data link layer addressing is added to enable a frame to be delivered to a destination node. A cyclic redundancy check (CRC) field is calculated on every bit and added to the frame. If the CRC value contained in the arriving frame is the same as the one the receiving node creates, the frame will be processed.
-
What will a host on an Ethernet network do if it receives a frame with a destination MAC address that does not match its own MAC address?
- It will discard the frame.
- It will forward the frame to the next host.
- It will remove the frame from the media.
- It will strip off the data-link frame to check the destination IP address.
Explanation: In an Ethernet network, each NIC in the network checks every arriving frame to see if the destination MAC address in the frame matches its own MAC address. If there is no match, the device discards the frame. If there is a match, the NIC passes the frame up to the next OSI layer.
-
What are two actions performed by a Cisco switch? (Choose two.)
- building a routing table that is based on the first IP address in the frame header
- using the source MAC addresses of frames to build and maintain a MAC address table
- forwarding frames with unknown destination IP addresses to the default gateway
- utilizing the MAC address table to forward frames via the destination MAC address
- examining the destination MAC address to add new entries to the MAC address table
Explanation: Important actions that a switch performs are as follows:
- When a frame comes in, the switch examines the Layer 2 source address to build and maintain the Layer 2 MAC address table.
- It examines the Layer 2 destination address to determine how to forward the frame. When the destination address is in the MAC address table, then the frame is sent out a particular port. When the address is unknown, the frame is sent to all ports that have devices connected to that network.
-
What are two examples of the cut-through switching method? (Choose two.)
- store-and-forward switching
- fast-forward switching
- CRC switching
- fragment-free switching
- QOS switching
Explanation: Store-and forward switching accepts the entire frame and performs error checking using CRC before forwarding the frame. Store-and-forward is often required for QOS analysis. Fast-forward and fragment-free are both variations of the cut-through switching method where only part of the frame is received before the switch begins to forward it.
-
Refer to the exhibit. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
- DD:DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
- 172.168.10.99
- CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC
- 172.168.10.65
- BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB
- AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
Explanation: When a host sends information to a distant network, the Layer 2 frame header will contain a source and destination MAC address. The source address will be the originating host device. The destination address will be the router interface that connects to the same network. In the case of host A sending information to host B, the source address is AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA and the destination address is the MAC address assigned to the R2 Ethernet interface, BB:BB:BB:BB:BB:BB.
-
What are two services provided by the OSI network layer? (Choose two.)
- performing error detection
- routing packets toward the destination
- encapsulating PDUs from the transport layer
- placement of frames on the media
- collision detection
Explanation: The OSI network layer provides several services to allow communication between devices:
- addressing
- encapsulation
- routing
- de-encapsulation
Error detection, placing frames on the media, and collision detection are all functions of the data ink layer.
-
What information is added during encapsulation at OSI Layer 3?
- source and destination MAC
- source and destination application protocol
- source and destination port number
- source and destination IP address
Explanation: IP is a Layer 3 protocol. Layer 3 devices can open the Layer 3 header to inspect the Layer 3 header which contains IP-related information including the source and destination IP addresses.
-
What are two functions of NVRAM? (Choose two.)
- to store the routing table
- to retain contents when power is removed
- to store the startup configuration file
- to contain the running configuration file
- to store the ARP table
Explanation: NVRAM is permanent memory storage, so the startup configuration file is preserved even if the router loses power.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator for a small advertising company has chosen to use the 192.168.5.96/27 network for internal LAN addressing. As shown in the exhibit, a static IP address is assigned to the company web server. However, the web server cannot access the Internet. The administrator verifies that local workstations with IP addresses that are assigned by a DHCP server can access the Internet, and the web server is able to ping local workstations. Which component is incorrectly configured?
- subnet mask
- DNS address
- host IP address
- default gateway address
Explanation: When a 255.255.255.224 subnet mask is used, the first three bits of the last octet are part of the network portion for an IPv4 address in the subnet. For the 192.168.5.96/27 network, valid host addresses are 192.168.5.97 through 192.168.5.126. The default gateway address is for the Layer 3 device on the same network and it must contain an IP address within the valid IP address range.
-
Why does a Layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP address and subnet mask?
- to identify the broadcast address of the destination network
- to identify the host address of the destination host
- to identify faulty frames
- to identify the network address of the destination network
Explanation: ANDing allows us to identify the network address from the IP address and the network mask.
-
What are the three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for internal private use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 64.100.0.0/14
- 127.16.0.0/12
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.31.7.0/24
- 192.168.0.0/16
Explanation: The private IP address blocks that are used inside companies are as follows:
- 10.0.0.0 /8 (any address that starts with 10 in the first octet)
- 172.16.0.0 /12 (any address that starts with 172.16 in the first two octets through 172.31.255.255)
- 192.168.0.0 /16 (any address that starts with 192.168 in the first two octets)
-
Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
- 198.133.219.17
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117
- 192.15.301.240
- 64.104.78.227
-
What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
- loopback
- link-local
- multicast
- global unicast
Explanation: Link-local IPv6 addresses start with FE80::/10, which is any address from FE80:: to FEBF::. Link-local addresses are used extensively in IPv6 and allow directly connected devices to communicate with each other on the link they share.
-
Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the output, which two statements about network connectivity are correct? (Choose two.)
- There is connectivity between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The connectivity between these two hosts allows for videoconferencing calls.
- There are 4 hops between this device and the device at 192.168.100.1.
- The average transmission time between the two hosts is 2 milliseconds.
- This host does not have a default gateway configured.
Explanation: The output displays a successful Layer 3 connection between a host computer and a host at 19.168.100.1. It can be determined that 4 hops exist between them and the average transmission time is 1 milliseconds. Layer 3 connectivity does not necessarily mean that an application can run between the hosts.
-
Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
Explanation: For the subnet of 192.168.1.64/26, there are 6 bits for host addresses, yielding 64 possible addresses. However, the first and last subnets are the network and broadcast addresses for this subnet. Therefore, the range of host addresses for this subnet is 192.168.1.65 to 192.168.1.126. The other subnets do not contain the address 192.168.1.96 as a valid host address.
-
How many hosts are addressable on a network that has a mask of 255.255.255.248?
- 2
- 6
- 8
- 14
- 16
- 254
Explanation: The subnet mask of 255.255.255.248 is the same as /29. This means the network portion of the address is 29 of the 32 bits in the address. Only 3 bits remain for host bits. 2^3 = 8, but one of these addresses has to be used for the network number and one address must be used as the broadcast address to reach all of the hosts on this network. That leaves only 6 usable IP addresses that can be assigned to hosts in this network. Don’t forget that the default gateway must be one of these devices if this network is to communicate with other networks.
-
Which statement is true about variable-length subnet masking?
- Each subnet is the same size.
- The size of each subnet may be different, depending on requirements.
- Subnets may only be subnetted one additional time.
- Bits are returned, rather than borrowed, to create additional subnets.
Explanation: In variable-length subnet masking, bits are borrowed to create subnets. Additional bits may be borrowed to create additional subnets within the original subnets. This may continue until there are no bits available to borrow.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address of 192.168.10.0/24 that has been assigned to a high school building. The largest network in this building has 100 devices. If 192.168.10.0 is the network number for the largest network, what would be the network number for the next largest network, which has 40 devices?
- 192.168.10.0
- 192.168.10.128
- 192.168.10.192
- 192.168.10.224
- 192.168.10.240
Explanation: The first thing to calculate is what IP addresses are used by the largest LAN. Because the LAN has 100 hosts, 7 bits must be left for host bits. This would be a subnet mask of 255.255.255.128 for the largest LAN (192.168.10.0/25). The IP addresses range from 192.168.10.0 through 192.168.10.127. 192.168.10.0 is the network number (all 0s in the host bits) and 192.168.10.127 is the broadcast for this Ethernet LAN (all 1s in the host bits). The next available IP address is the next network number – 192.168.10.128.
-
In what two situations would UDP be the preferred transport protocol over TCP? (Choose two.)
- when applications need to guarantee that a packet arrives intact, in sequence, and unduplicated
- when a faster delivery mechanism is needed
- when delivery overhead is not an issue
- when applications do not need to guarantee delivery of the data
- when destination port numbers are dynamic
Explanation: UDP is a stateless protocol, which means that neither device on either end of the conversation must keep track of the conversation. As a stateless protocol, UDP is used as the Layer 4 protocol for applications that need speedy (best-effort) delivery. An example of such traffic is the transport of digitized voice or video.
-
What important information is added to the TCP/IP transport layer header to ensure communication and connectivity with a remote network device?
- timing and synchronization
- destination and source port numbers
- destination and source physical addresses
- destination and source logical network addresses
Explanation: The destination and source port numbers are used to identify exactly which protocol and process is requesting or responding to a request.
-
What is the TCP mechanism used in congestion avoidance?
- three-way handshake
- socket pair
- two-way handshake
- sliding window
Explanation: TCP uses windows to attempt to manage the rate of transmission to the maximum flow that the network and destination device can support while minimizing loss and retransmissions. When overwhelmed with data, the destination can send a request to reduce the of the window. This congestion avoidance is called sliding windows.
-
Which three statements characterize UDP? (Choose three.)
- UDP provides basic connectionless transport layer functions.
- UDP provides connection-oriented, fast transport of data at Layer 3.
- UDP relies on application layer protocols for error detection.
- UDP is a low overhead protocol that does not provide sequencing or flow control mechanisms.
- UDP relies on IP for error detection and recovery.
- UDP provides sophisticated flow control mechanisms.
Explanation: UDP is a simple protocol that provides the basic transport layer functions. It has much lower overhead than TCP because it is not connection-oriented and does not offer the sophisticated retransmission, sequencing, and flow control mechanisms that provide reliability.
-
Which two tasks are functions of the presentation layer? (Choose two.)
- compression
- addressing
- encryption
- session control
- authentication
Explanation: The presentation layer deals with common data format. Encryption, formatting, and compression are some of the functions of the layer. Addressing occurs in the network layer, session control occurs in the session layer, and authentication takes place in the application or session layer.
-
Which two protocols operate at the highest layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack? (Choose two.)
- DNS
- Ethernet
- IP
- POP
- TCP
- UDP
Explanation: The application layer is the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack. Application layer protocols include HTTP, DNS, HTML, TFTP, POP, IMAP, FTP, and SMTP.
-
Which two roles can a computer assume in a peer-to-peer network where a file is being shared between two computers? (Choose two.)
- client
- master
- server
- slave
- transient
Explanation: In a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, two or more computers are connected and can share resources without the use of a dedicated server. The computer that has the file acts as a server for the device (the client) that requests the file.
-
What is the function of the HTTP GET message?
- to request an HTML page from a web server
- to send error information from a web server to a web client
- to upload content to a web server from a web client
- to retrieve client email from an email server using TCP port 110
Explanation: There are three common HTTP message types:
- GET – used by clients to request data from the web server
- POST – used by clients to upload data to a web server
- PUT – used by clients to upload data to a web server
-
A wireless host needs to request an IP address. What protocol would be used to process the request?
- FTP
- HTTP
- DHCP
- ICMP
- SNMP
Explanation: The DHCP protocol is used to request, issue, and manage IP addressing information. CSMA/CD is the access method used with wired Ethernet. ICMP is used to test connectivity. SNMP is used with network management and FTP is used for file transfer.
-
When planning for network growth, where in the network should packet captures take place to assess network traffic?
- on as many different network segments as possible
- only at the edge of the network
- between hosts and the default gateway
- only on the busiest network segment
Explanation: Because some types of traffic will be only on specific network segments, packet captures for analysis should be performed on as many segments as possible.
-
When applied to a router, which command would help mitigate brute-force password attacks against the router?
- exec-timeout 30
- service password-encryption
- banner motd $Max failed logins = 5$
- login block-for 60 attempts 5 within 60
Explanation: The login block-for command sets a limit on the maximum number of failed login attempts allowed within a defined period of time. If this limit is exceeded, no further logins are allowed for the specified period of time. This helps to mitigate brute-force password cracking since it will significantly increase the amount of time required to crack a password. The exec-timeout command specifies how long the session can be idle before the user is disconnected. The service password-encryption command encrypts the passwords in the running configuration. The banner motd command displays a message to users who are logging in to the device.
-
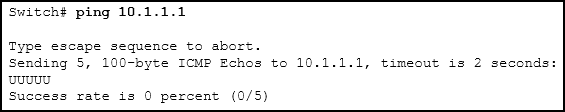
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is testing connectivity to a remote device with the IP address 10.1.1.1. What does the output of this command indicate?
- Connectivity to the remote device was successful.
- A router along the path did not have a route to the destination.
- A ping packet is being blocked by a security device along the path.
- The connection timed out while waiting for a reply from the remote device.
Explanation: In the output of the ping command, an exclamation mark (!) indicates a response was successfully received, a period (.) indicates that the connection timed out while waiting for a reply, and the letter “U” indicates that a router along the path did not have a route to the destination and sent an ICMP destination unreachable message back to the source.
-
A user is unable to reach the web site when typing http://www.cisco.com in a web browser, but can reach the same site by typing http://72.163.4.161. What is the issue?
- default gateway
- DHCP
- DNS
- TCP/IP protocol stack
Explanation: Domain Name Service (DNS) is used to translate a web address to an IP address. The address of the DNS server is provided via DHCP to host computers.
-
What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
- the highest configured IP address on the router
- a loopback IP address
- the IP address of the outbound interface
- the lowest configured IP address on the router
Explanation: When sending an echo request message, a router will use the IP address of the exit interface as the source IP address. This default behavior can be changed by using an extended ping and specifying a specific source IP address.
-
Match each item to the type of topology diagram on which it is typically identified. (Not all options are used.)
Explanation: A logical topology diagram typically depicts the IP addressing scheme and groupings of devices and ports. A physical topology diagram shows how those devices are connected to each other and the network, focusing on the physical locations of intermediary devices, configured ports, and cabling.
-
Match the description with the associated IOS mode. (Not all options are used.)
-
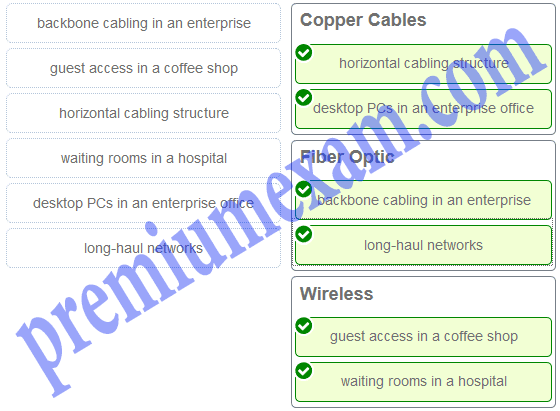
Match the situation with the appropriate use of network media.
Explanation: Copper Cables – horizontal cabling structure and desktop PCs in offices in an enterprise
Fiber optic – backbone cabling in an enterprise and long-haul networks
Wireless – coffee shops and waiting rooms in a hospital -
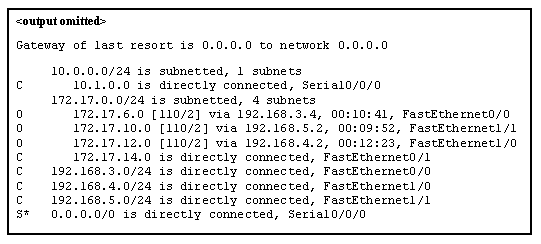
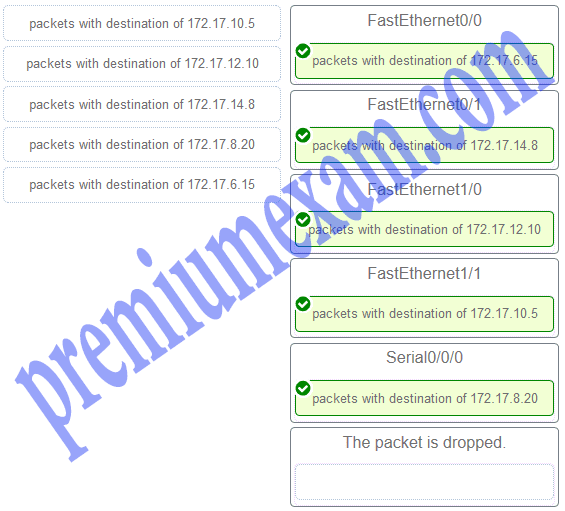
Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
Explanation:
Packets with a destination of 172.17.6.15 are forwarded through Fa0/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.10.5 are forwarded through Fa1/1. Packets with a destination of 172.17.12.10 are forwarded through Fa1/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.14.8 are forwarded through Fa0/1. Because network 172.17.8.0 has no entry in the routing table, it will take the gateway of last resort, which means that packets with a destination of 172.17.8.20 are forwarded through Serial0/0/0. Because a gateway of last resort exists, no packets will be dropped.